Description
PAF is a potent phospholipid mediator which exerts diverse biological actions by interaction with a G protein-coupled PAF receptor. The PAF receptor has been cloned from a number of species including human, rat, and guinea pig and is characterized as a 7-transmembrane receptor which induces phosphoinositol turnover through G-protein coupling.{5109,5148,5150,5145,5149} Northern blot analysis reveals that the receptor is expressed in leukocytes, placenta, lung, spleen, small intestine, kidney, liver, and brain.{5150,5145} In leukocyte cell populations the receptor is found on platelets, monocytes, neutrophils, and B-cells, whereas resting T-cells and natural killer cell lines do not express the PAF receptor.{4226} Human monocytes treated with INF-γ have a 2-6 fold increase in PAF receptor expression compared to untreated cells.{4225}
Synonyms: Platelet-activating Factor Receptor
Immunogen: Synthetic peptide from the internal region of human PAF receptor
Formulation: 100 µg of Protein A-purified monoclonal antibody
Isotype: IgG2a
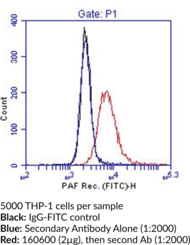
Applications: (+) ELISA, FC, and ICC; (−) WB
Origin: Animal/Mouse
Stability: 730 days
Application|ELISA||Application|Flow Cytometry||Application|Immunocytochemistry||Product Type|Antibodies|Monoclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Blood|Coagulation & Hemostasis||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry|Glycerophospholipids