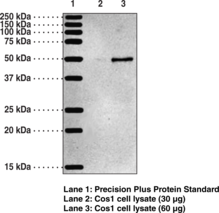
Description
SMAD3, a member of the SMAD family of proteins, is involved in the TGF-β signaling cascade. A human homolog of Drosophila Mad protein, SMAD3 consists of an N-terminal DNA-binding MH1 domain, a linker region and a C-terminal MH2 domain. It is a receptor-regulated SMAD (R-SMAD) that functions downstream of TGF-β and activin receptors and mediates their signaling.{19270,19289} It is recruited by SARA (SMAD anchor for receptor activation) to the receptor kinase for phosphorylation. Upon phosphorylation, SMAD3 dissociates from SARA, forms a complex with SMAD4 and transmigrates into the nucleus where it complexes with other cofactors and acts as a transcription factor. It has an indispensable role in cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis and formation of ECM. Loss of SMAD3 results in childhood T cell leukemia.
Synonyms:
Immunogen: Portion of amino acids 100-150 of human SMAD3
Formulation: 100 µg protein G-purified IgG
Isotype:
Applications: IF, IHC, and WB
Origin: Animal/Rabbit
Stability: 180 days
Application|Immunofluorescence||Application|Immunohistochemistry||Application|Western Blot||Product Type|Antibodies|Polyclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Cancer||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Death|Apoptosis||Research Area|Epigenetics, Transcription, & Translation|Transcription Factors